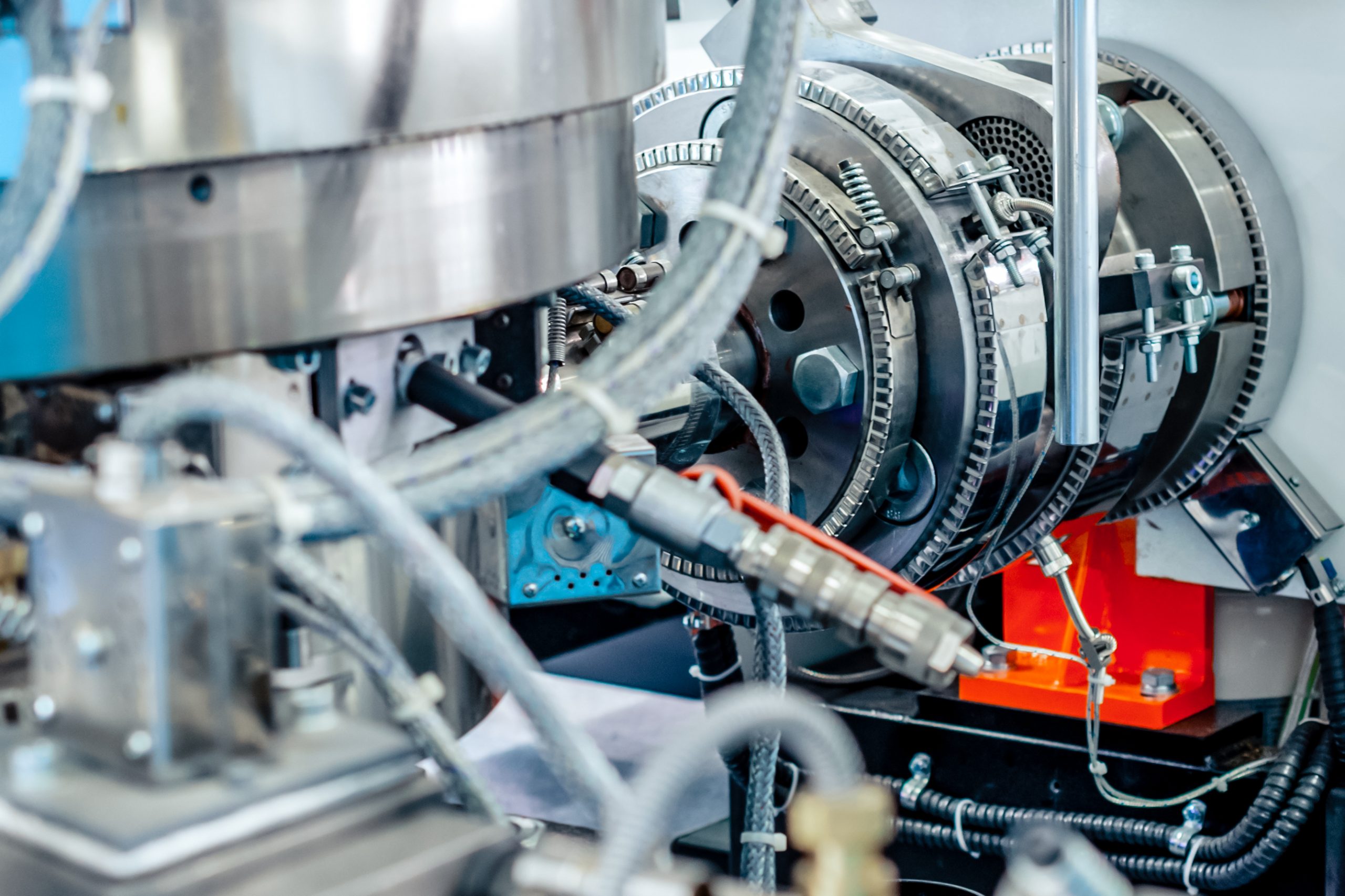
Injection molding plants are busy environments where safety is paramount. The complex machinery, high temperatures, and hazardous materials used in the process pose significant risks to workers. Adhering to stringent safety standards not only protects employees but also enhances operational efficiency and compliance with regulatory requirements. Here’s an overview of the essential safety standards and practices for injection molding plants.
Understanding the Importance of Safety Standards
Safety standards in injection molding plants are designed to prevent accidents, injuries, and illnesses. They encompass a wide range of measures, from equipment maintenance and worker training to emergency preparedness and ergonomics. Implementing these standards ensures a safe working environment, reduces downtime, and fosters a culture of safety.
Key Safety Standards and Practices
1. Machine Safety
Injection molding machines are powerful and potentially dangerous if not handled correctly. Ensuring machine safety involves:
- Guarding and Barriers: Install proper guarding and barriers around moving parts to prevent accidental contact.
- Interlock Systems: Use interlock systems to ensure machines cannot operate unless guards are in place.
- Regular Maintenance: Perform routine maintenance and inspections to identify and address potential hazards.
- Lockout/Tagout (LOTO): Implement LOTO procedures to ensure machines are properly shut off and unable to restart during maintenance.
2. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Wearing appropriate PPE is crucial for protecting workers from injuries and exposure to hazardous substances. Essential PPE includes:
- Gloves: To protect hands from cuts, burns, and chemical exposure.
- Safety Glasses: To shield eyes from flying debris and splashes.
- Face Shields: For additional face protection during certain operations.
- Heat-Resistant Clothing: To guard against burns from hot materials and surfaces.
- Respirators: When dealing with fumes, dust, or other airborne hazards.
3. Training and Education
Well-trained employees are better equipped to recognize hazards and follow safety protocols. Key training areas include:
- Machine Operation: Detailed instruction on operating machines safely and efficiently.
- Emergency Procedures: Training on how to respond to fires, spills, and other emergencies.
- Hazard Communication: Understanding Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) and the risks associated with chemicals used in the plant.
- First Aid: Basic first aid training to handle minor injuries and stabilize severe ones until professional help arrives.
4. Ergonomics
Ergonomic practices reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders and enhance worker comfort and productivity. Implementing ergonomics involves:
- Workstation Design: Adjust workstations to fit the needs of individual workers, minimizing strain.
- Proper Lifting Techniques: Train employees on safe lifting methods to prevent back injuries.
- Anti-Fatigue Mats: Use mats in areas where workers stand for long periods to reduce fatigue.
5. Chemical Safety
Handling chemicals safely is crucial in injection molding plants, where hazardous substances are often used. Essential practices include:
- Proper Storage: Store chemicals in designated areas with appropriate labeling and containment measures.
- Spill Response: Have spill response plans and materials readily available.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation to prevent the buildup of harmful fumes and vapors.
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Maintain accessible SDS for all chemicals, providing detailed safety information.
6. Emergency Preparedness
Being prepared for emergencies minimizes risks and ensures a swift, effective response. Key aspects include:
- Emergency Exits: Clearly mark and keep emergency exits unobstructed.
- Fire Safety: Install fire extinguishers, alarms, and sprinkler systems, and conduct regular fire drills.
- Emergency Plans: Develop and regularly update emergency response plans, covering a range of scenarios.
- First Aid Kits: Keep well-stocked first aid kits in easily accessible locations throughout the plant.
7. Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to local, state, and federal regulations is essential for maintaining a safe workplace. Key regulations include:
- OSHA Standards: Follow Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) guidelines for machine safety, PPE, ergonomics, and more.
- EPA Regulations: Comply with Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) standards for handling and disposing of hazardous materials.
- Industry Standards: Adhere to industry-specific safety standards and best practices, such as those from the Plastics Industry Association.
Conclusion
Ensuring safety in injection molding plants is a multifaceted effort that requires adherence to comprehensive standards and practices. By focusing on machine safety, PPE, training, ergonomics, chemical safety, emergency preparedness, and regulatory compliance, plants can create a secure working environment. Prioritizing safety not only protects employees but also enhances productivity, reduces downtime, and fosters a culture of safety that benefits the entire organization. Implementing these safety standards is an investment in the well-being of your workforce and the long-term success of your business.