Countless molders work day in and day out pushing buttons but not totally understanding how injection molding machines work, so we wanted to take a step back and review the basics in order to build a strong foundation of knowledge. Understanding how plastic injection molding machines work can shed light on the intricate process that brings countless everyday items to life. Here’s a detailed look at the components and operation of a plastic injection molding machine.
Components of a Plastic Injection Molding Machine
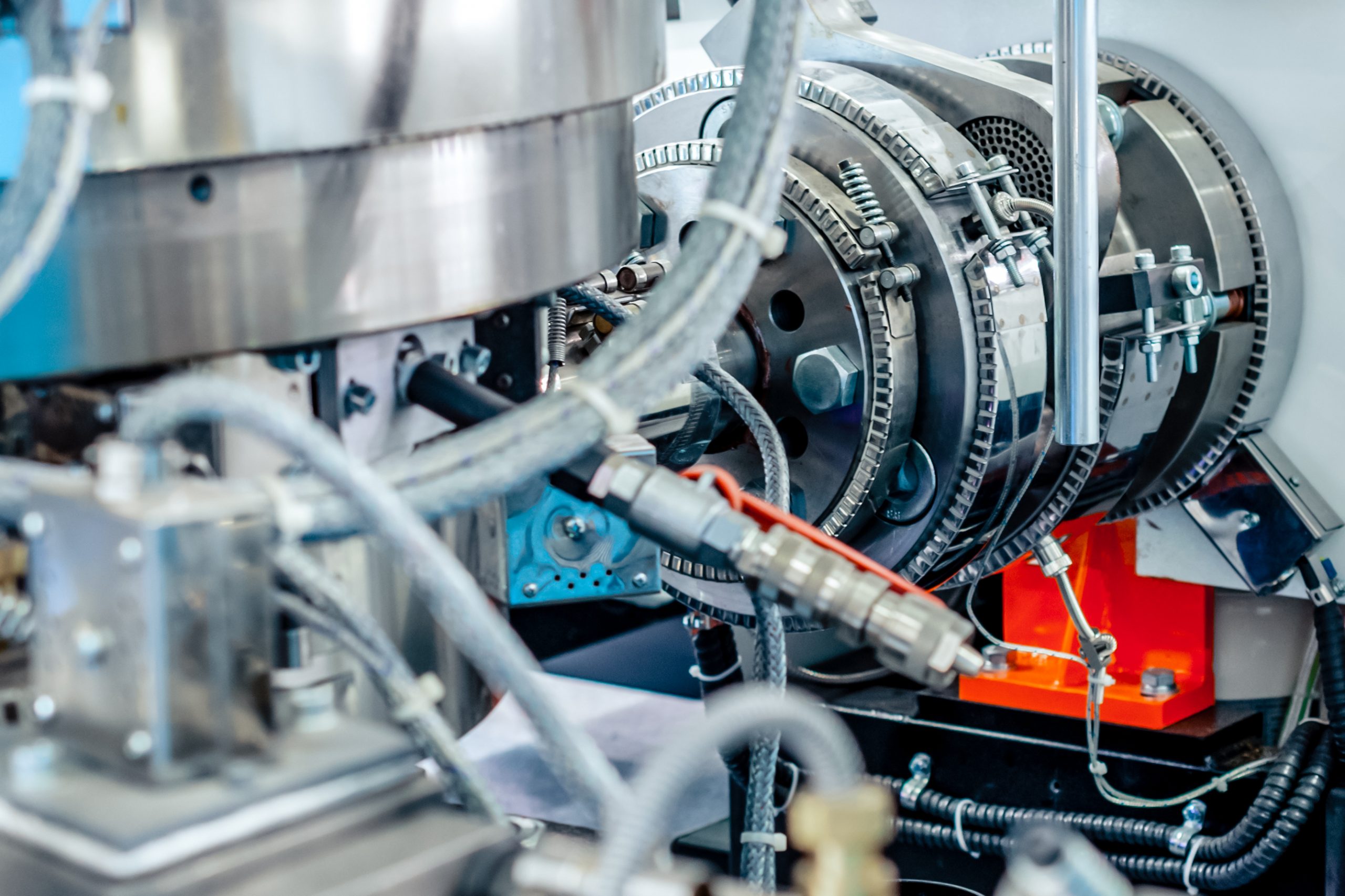
An injection molding machine consists of three primary sections: the injection unit, the mold, and the clamping unit. Each plays a crucial role in the overall process.
1. The Injection Unit
The injection unit is where the plastic is melted, mixed, and injected into the mold. It includes several key components:
- Hopper: This is the container that holds the raw plastic pellets or granules. These materials are gravity-fed into the barrel of the machine.
- Barrel: The barrel is a heated cylinder where the plastic is melted. The temperature is precisely controlled to ensure the plastic reaches the correct viscosity.
- Screw: Inside the barrel is a screw that rotates to move, melt, and mix the plastic. The screw design is critical for efficient melting and homogenization of the plastic material.
- Nozzle: The nozzle directs the molten plastic from the barrel into the mold. It must be designed to prevent leakage and ensure a consistent flow of plastic.
2. The Mold
The mold is a custom-designed tool that shapes the molten plastic into the desired part. It has two halves:
- Stationary (Fixed) Half: Attached to the injection unit, this half remains fixed in place.
- Moving Half: Attached to the clamping unit, this half moves to open and close the mold. The design of the mold is critical for ensuring the final product’s precision and quality.
3. The Clamping Unit
The clamping unit holds the mold halves together during the injection and cooling process. Key components include:
- Clamping Mechanism: Applies the necessary force to keep the mold halves tightly closed. There are various types of clamping mechanisms, including hydraulic, mechanical, and toggle systems.
- Ejector System: After the plastic part has solidified, the ejector system pushes the part out of the mold. This is usually achieved with ejector pins that apply force to release the part.
The Injection Molding Process
The plastic injection molding process involves several precise steps, each critical for ensuring the quality and consistency of the final product.
1. Clamping
The process begins with the clamping unit closing the mold halves. The clamping mechanism applies significant force to keep the mold securely closed, which is essential to withstand the pressure of the injected plastic.
2. Injection
Once the mold is clamped, the injection phase begins. The screw inside the barrel moves forward, pushing the molten plastic through the nozzle into the mold cavity. The plastic is injected under high pressure to ensure it fills the entire cavity and captures every detail of the mold design.
3. Cooling
As the molten plastic fills the mold, it begins to cool and solidify. The cooling time depends on the part’s thickness and the type of plastic used. Efficient cooling is crucial for maintaining the part’s dimensions and quality. Some molds have cooling channels to speed up this process.
4. Ejection
After the part has sufficiently cooled and solidified, the mold opens. The ejector system is activated, using ejector pins to push the part out of the mold. The mold then closes again, and the cycle repeats for the next part.
5. Repeat
The injection molding cycle is highly efficient, often taking only seconds to minutes per part, depending on the complexity and size of the item being produced. This rapid cycle time is one of the reasons injection molding is suitable for high-volume production.
Optimizing Injection Molding
Several factors can influence the efficiency and quality of the injection molding process:
- Material Selection: Choosing the right plastic material is crucial. Different plastics have varying properties that affect melting temperature, flow characteristics, and cooling time.
- Machine Settings: Precise control of temperature, pressure, and timing is essential. Modern injection molding machines often feature advanced control systems for fine-tuning these parameters.
- Mold Design: The design and construction of the mold are critical. Proper venting, cooling channels, and gating systems all impact the quality of the final part.
Conclusion
The plastic injection molding machine is a marvel of modern engineering, capable of producing complex and precise plastic parts with remarkable efficiency. By understanding how each component works and the steps involved in the injection molding process, manufacturers can optimize production, reduce waste, and ensure high-quality output. As technology advances, injection molding continues to evolve, offering even greater capabilities and applications in the world of manufacturing.
Want to learn more? Check out our training courses!